Have you ever wondered how Artificial Intelligence (AI) seems to "think" and make decisions? It might sound complex, but at its core, AI's decision-making often boils down to a concept we use every day: the "if-then" rule.
Let's break it down in a simple way, comparing it to how we humans make choices.
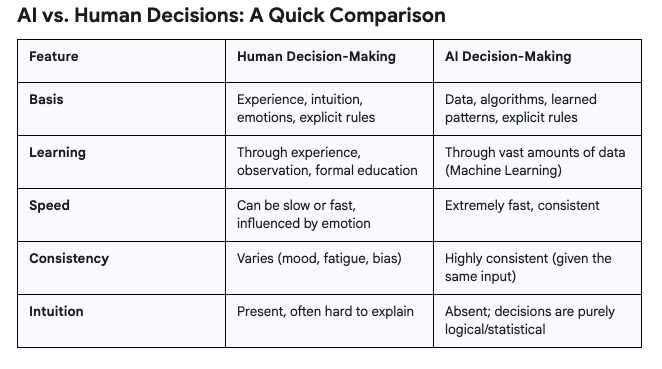
How Do We Humans Decide?
Imagine you're deciding whether to take an umbrella with you. Your brain quickly processes information:
- If it's raining outside, then take an umbrella.
- If the sky is dark and cloudy, then consider taking an umbrella.
- If the weather app says rain, then definitely take an umbrella.
We combine these "if-then" rules with our past experiences, our intuition, and the information available to us to arrive at a decision. It's a mix of learned patterns and gut feelings.
AI's Decision-Making: The "If-Then" Core
AI, in its most fundamental form, operates on similar "if-then" logic, but without the "gut feeling" part.
- Simple Rules (Early AI):
In the early days, AI systems were explicitly programmed with rules. For example, a simple spam filter might have a rule like:
- If an email contains "free money" then mark it as spam.
This works for clear cases, but what about more subtle spam? That's where learning comes in.
2. Learning the Rules (Modern AI):
Modern AI, especially through Machine Learning (ML), isn't just given a list of rules; it learns them from data. Think of it like teaching a child to recognize a cat:
- You show the child many pictures: "This is a cat," "This is not a cat."
- The child's brain starts to identify patterns: "If it has pointy ears, whiskers, and says 'meow,' then it's a cat."
AI learns in a similar way. You feed an AI model vast amounts of data (e.g., millions of images labeled "cat" or "not cat"). The AI's algorithms then analyze this data to discover the underlying patterns and relationships. It essentially builds its own complex set of "if-then" rules.So, for an image recognition AI, it might learn:
If the pixel patterns resemble a feline shape, with specific textures for fur and distinct eye structures, then classify it as a "cat" with X% certainty.
3. The Role of Data: AI's "Experience"
Just like a human needs experience to make better decisions, AI needs data. The more diverse and accurate the data an AI learns from, the smarter and more precise its "if-then" rules become. Data is the "experience" that allows AI to refine its understanding of the world.
4. Beyond Simple Rules: Complex Learning
For more advanced AI, like the large language models (LLMs) that power conversational AI, the "if-then" rules become incredibly intricate and layered. Instead of simple, direct rules, AI builds complex networks (like neural networks) that can identify subtle correlations and patterns that no human could explicitly program. It's still "if this pattern, then that outcome," but on a massive, nuanced scale.
The Takeaway
While AI might seem like magic, its decision-making process is fundamentally logical and data-driven. It's about processing information and applying learned "if-then" patterns with incredible speed and consistency. Understanding this core concept is your first step to demystifying the world of AI!


